Bootstrap 5
https://getbootstrap.com/docs/5.0/getting-started/introduction/
https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.0.2/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css
Jquery
https://jquery.com/download/
CDN : jsDelivr CDN
https://www.jsdelivr.com/package/npm/jquery
https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/jquery@3.6.0/dist/jquery.min.js
Datatables
https://datatables.net/
DataTables is a plug-in for the jQuery Javascript library. It is a highly flexible tool, built upon the foundations of progressive enhancement, that adds all of these advanced features to any HTML table.
Connect to MySQL Database
devtest/settings.py
//devproject/settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'myapp', #add myapp
]
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
'NAME': 'django',
'USER': 'root',
'PASSWORD': '',
'HOST': 'localhost',
'PORT': '3306'
}
}
Model Class
//myapp/models.py from django.db import models # Create your models here. class User(models.Model): id = models.IntegerField() name = models.CharField(max_length=50) email = models.CharField(max_length=100) phone = models.IntegerField(max_length=10) address = models.CharField(max_length=250) class Meta: db_table = "user" app_label = '' def __str__(self): return selfdatabase user table
//database user table CREATE TABLE `user` ( `id` int unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(50) NOT NULL, `email` varchar(100) NOT NULL, `phone` int unsigned NOT NULL, `address` varchar(250) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci; insert into `user`(`id`,`name`,`email`,`phone`,`address`) values (1,'cairocoders','cairocoders@gmail.com',2147483647,'Olongapo City'), (2,'tutorial101','turorial101@gmail.com',34256780,'Olongapo City');Make Migrations
Run the commands below to make migrations:
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
C:\my_project_django\testdev>python manage.py makemigrations
C:\my_project_django\testdev>python manage.py migrate
Creating View
myapp/views.py
//myapp/views.py
from django.http import HttpResponse
from django.template import loader
from django.shortcuts import render
from .models import User
def index(request):
user_list = User.objects.order_by('id')
#template = loader.get_template('index.html')
#context = {
# 'user_list': user_list,
#}
#return HttpResponse(template.render(context, request))
context = {'user_list': user_list}
return render(request, 'index.html', context)
myapp/urls.py
//myapp/urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from myapp import views #add myapp
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('', views.index, name='index')
]
myapp/templates/index.html
//myapp/templates/index.html
{% extends "base.html" %}
{% block content %}
{% if user_list %}
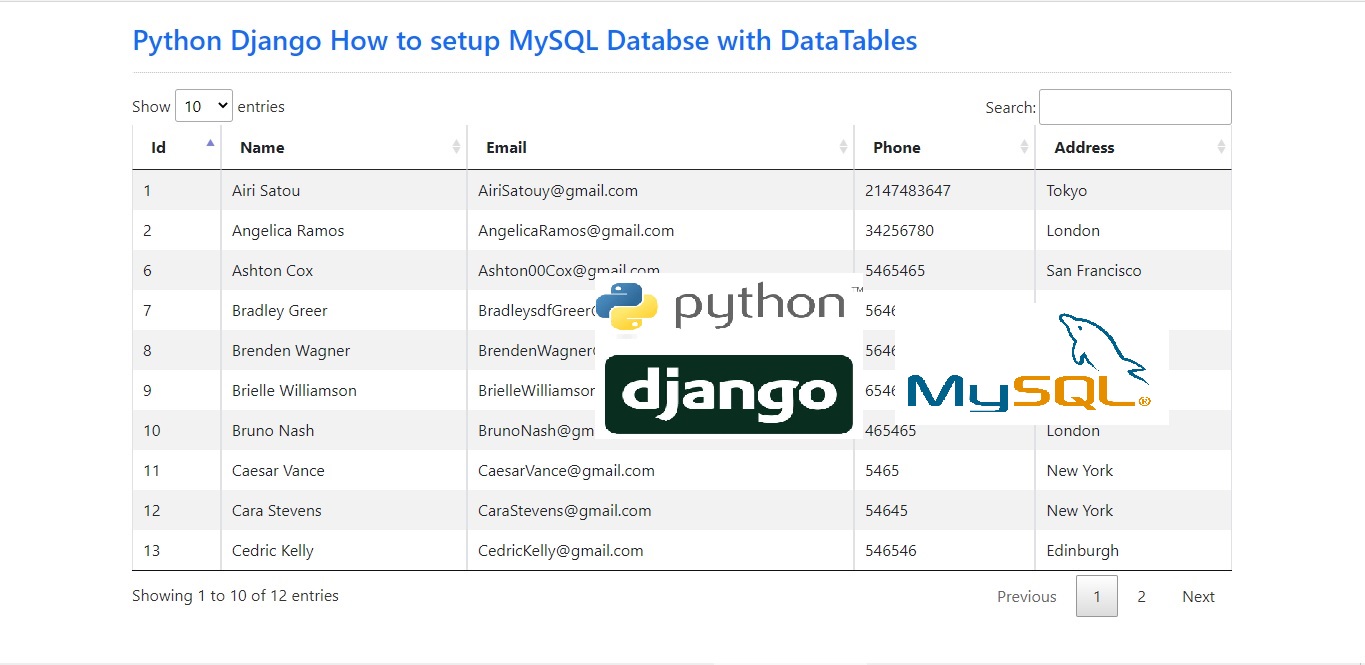
<table id="table" class="table table-bordered table-striped">
<thead>
<th>Id</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Email</th>
<th>Phone</th>
<th>Address</th>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for user in user_list %}
<tr>
<td>{{user.id}}</td>
<td>{{user.name}}</td>
<td>{{user.email}}</td>
<td>{{user.phone}}</td>
<td>{{user.address}}</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
{% else %}
<p>No user record available</p>
{% endif %}
{% endblock %}
myapp/templates/base.html
//myapp/templates/base.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"/>
<title>Python Django How to setup MySQL Databse</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.0.2/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<link rel = "stylesheet" type = "text/css" href = "https://cdn.datatables.net/1.11.5/css/jquery.dataTables.min.css"/>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container" style="padding:20px;">
<div class="col-12">
<h3 class="text-primary">Python Django How to setup MySQL Databse with DataTables</h3>
<hr style="border-top:1px dotted #ccc;"/>
{% block content %} {% endblock %}
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/jquery@3.6.0/dist/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src = "https://cdn.datatables.net/1.11.5/js/jquery.dataTables.min.js"></script>
<script type = "text/javascript">
$(document).ready(function(){
$('#table').DataTable();
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Run : C:\django\devproject>python manage.py runserver