1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 | from __future__ import division # So that 8/3 will be 2.6666 and not 2import wxfrom math import * # So we can evaluate "sqrt(8)"class Calculator(wx.Dialog): '''Main calculator dialog''' def __init__(self): wx.Dialog.__init__(self, None, -1, "Calculator") sizer = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL) # Main vertical sizer # ____________v self.display = wx.ComboBox(self, -1) # Current calculation sizer.Add(self.display, 0, wx.EXPAND) # Add to main sizer # [7][8][9][/] # [4][5][6][*] # [1][2][3][-] # [0][.][C][+] gsizer = wx.GridSizer(4, 4) for row in (("7", "8", "9", "/"), ("4", "5", "6", "*"), ("1", "2", "3", "-"), ("0", ".", "C", "+")): for label in row: b = wx.Button(self, -1, label) gsizer.Add(b) self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnButton, b) sizer.Add(gsizer, 1, wx.EXPAND) # [ = ] b = wx.Button(self, -1, "=") self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnButton, b) sizer.Add(b, 0, wx.EXPAND) self.equal = b # Set sizer and center self.SetSizer(sizer) sizer.Fit(self) self.CenterOnScreen() def OnButton(self, evt): '''Handle button click event''' # Get title of clicked button label = evt.GetEventObject().GetLabel() if label == "=": # Calculate try: compute = self.display.GetValue() # Ignore empty calculation if not compute.strip(): return # Calculate result result = eval(compute) # Add to history self.display.Insert(compute, 0) # Show result self.display.SetValue(str(result)) except Exception, e: wx.LogError(str(e)) return elif label == "C": # Clear self.display.SetValue("") else: # Just add button text to current calculation self.display.SetValue(self.display.GetValue() + label) self.equal.SetFocus() # Set the [=] button in focusif __name__ == "__main__": # Run the application app = wx.App() dlg = Calculator() dlg.ShowModal() dlg.Destroy() |
article
Showing posts with label python-wxPython. Show all posts
Showing posts with label python-wxPython. Show all posts
Sunday, May 27, 2018
wxpython Calculator
wxpython Calculator
wxpython layout wx.GridSizer
wxpython layout wx.GridSizer
The wx.GridSizer lays out widgets in two dimensional table. Each cell within the table has the same size.
wx.GridSizer(int rows=1, int cols=0, int vgap=0, int hgap=0)
The wx.GridSizer lays out widgets in two dimensional table. Each cell within the table has the same size.
wx.GridSizer(int rows=1, int cols=0, int vgap=0, int hgap=0)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 | import wxclass Example(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, parent, title): super(Example, self).__init__(parent, title=title, size=(300, 250)) self.InitUI() self.Centre() self.Show() def InitUI(self): menubar = wx.MenuBar() fileMenu = wx.Menu() menubar.Append(fileMenu, '&File') self.SetMenuBar(menubar) vbox = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL) self.display = wx.TextCtrl(self, style=wx.TE_RIGHT) vbox.Add(self.display, flag=wx.EXPAND|wx.TOP|wx.BOTTOM, border=4) gs = wx.GridSizer(5, 4, 5, 5) gs.AddMany( [(wx.Button(self, label='Cls'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='Bck'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.StaticText(self), wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='Close'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='7'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='8'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='9'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='/'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='4'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='5'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='6'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='*'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='1'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='2'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='3'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='-'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='0'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='.'), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='='), 0, wx.EXPAND), (wx.Button(self, label='+'), 0, wx.EXPAND) ]) vbox.Add(gs, proportion=1, flag=wx.EXPAND) self.SetSizer(vbox)if __name__ == '__main__': app = wx.App() Example(None, title='Calculator') app.MainLoop() |
wxpython layout Absolute Positioning
wxpython layout Absolute Positioning
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 | import wxclass Example(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, parent, title): super(Example, self).__init__(parent, title=title, size=(260, 180)) self.InitUI() self.Centre() self.Show() def InitUI(self): menubar = wx.MenuBar() filem = wx.Menu() editm = wx.Menu() helpm = wx.Menu() menubar.Append(filem, '&File') menubar.Append(editm, '&Edit') menubar.Append(helpm, '&Help') self.SetMenuBar(menubar) #wx.TextCtrl(panel, pos=(3, 3), size=(250, 150)) wx.TextCtrl(self) #auto reizeif __name__ == '__main__': app = wx.App() Example(None, title='Absolute Positioning') app.MainLoop() |
wxpython enable and disable toolbar buttons
wxpython enable and disable toolbar buttons
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 | import wxclass Example(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs) self.InitUI() def InitUI(self): self.count = 5 self.toolbar = self.CreateToolBar() tundo = self.toolbar.AddLabelTool(wx.ID_UNDO, '', wx.Bitmap('img/blogger.png')) tredo = self.toolbar.AddLabelTool(wx.ID_REDO, '', wx.Bitmap('img/youtube.png')) self.toolbar.EnableTool(wx.ID_REDO, False) self.toolbar.AddSeparator() texit = self.toolbar.AddLabelTool(wx.ID_EXIT, '', wx.Bitmap('img/icon_shortcut_tickets.png')) self.toolbar.Realize() self.Bind(wx.EVT_TOOL, self.OnQuit, texit) self.Bind(wx.EVT_TOOL, self.OnUndo, tundo) self.Bind(wx.EVT_TOOL, self.OnRedo, tredo) self.SetSize((250, 200)) self.SetTitle('Undo redo') self.Centre() self.Show(True) def OnUndo(self, e): if self.count > 1 and self.count <= 5: self.count = self.count - 1 if self.count == 1: self.toolbar.EnableTool(wx.ID_UNDO, False) if self.count == 4: self.toolbar.EnableTool(wx.ID_REDO, True) def OnRedo(self, e): if self.count < 5 and self.count >= 1: self.count = self.count + 1 if self.count == 5: self.toolbar.EnableTool(wx.ID_REDO, False) if self.count == 2: self.toolbar.EnableTool(wx.ID_UNDO, True) def OnQuit(self, e): self.Close()def main(): ex = wx.App() Example(None) ex.MainLoop() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
wxpython create more than one toolbars example
wxpython create more than one toolbars example
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 | import wxclass Example(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs) self.InitUI() def InitUI(self): vbox = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL) #create two horizontal toolbars toolbar1 = wx.ToolBar(self) toolbar1.AddLabelTool(wx.ID_ANY, '', wx.Bitmap('img/icon_shortcut_contacts.png')) toolbar1.AddLabelTool(wx.ID_ANY, '', wx.Bitmap('img/icon_shortcut_looong.png')) toolbar1.AddLabelTool(wx.ID_ANY, '', wx.Bitmap('img/icon_shortcut_sales.png')) toolbar1.Realize() toolbar2 = wx.ToolBar(self) qtool = toolbar2.AddLabelTool(wx.ID_EXIT, '', wx.Bitmap('img/icon_shortcut_tickets.png')) toolbar2.Realize() vbox.Add(toolbar1, 0, wx.EXPAND) vbox.Add(toolbar2, 0, wx.EXPAND) self.Bind(wx.EVT_TOOL, self.OnQuit, qtool) self.SetSizer(vbox) self.SetSize((300, 250)) self.SetTitle('Toolbars') self.Centre() self.Show(True) def OnQuit(self, e): self.Close()def main(): ex = wx.App() Example(None) ex.MainLoop() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
Friday, June 10, 2016
wxpython widgets wx.ListCtrl
wxpython widgets wx.ListCtrl
A wx.ListCtrl is a graphical representation of a list of items
wx.ListCtrl styles
wx.LC_LIST
wx.LC_REPORT
wx.LC_VIRTUAL
wx.LC_ICON
wx.LC_SMALL_ICON
wx.LC_ALIGN_LEFT
wx.LC_EDIT_LABELS
wx.LC_NO_HEADER
wx.LC_SORT_ASCENDING
wx.LC_SORT_DESCENDING
wx.LC_HRULES
wx.LC_VRULES
A wx.ListCtrl is a graphical representation of a list of items
wx.ListCtrl styles
wx.LC_LIST
wx.LC_REPORT
wx.LC_VIRTUAL
wx.LC_ICON
wx.LC_SMALL_ICON
wx.LC_ALIGN_LEFT
wx.LC_EDIT_LABELS
wx.LC_NO_HEADER
wx.LC_SORT_ASCENDING
wx.LC_SORT_DESCENDING
wx.LC_HRULES
wx.LC_VRULES
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 | import wximport syspackages = [('jessica alba', 'pomona', '1981'), ('sigourney weaver', 'new york', '1949'), ('angelina jolie', 'los angeles', '1975'), ('natalie portman', 'jerusalem', '1981'), ('rachel weiss', 'london', '1971'), ('scarlett johansson', 'new york', '1984' )]class Actresses(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, parent, id, title): wx.Frame.__init__(self, parent, id, title, size=(380, 230)) hbox = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL) panel = wx.Panel(self, -1) self.list = wx.ListCtrl(panel, -1, style=wx.LC_REPORT) #We create a wx.ListCtrl with a wx.LC_REPORT style self.list.InsertColumn(0, 'name', width=140) self.list.InsertColumn(1, 'place', width=130) self.list.InsertColumn(2, 'year', wx.LIST_FORMAT_RIGHT, 90) for i in packages: index = self.list.InsertStringItem(sys.maxint, i[0]) self.list.SetStringItem(index, 1, i[1]) self.list.SetStringItem(index, 2, i[2]) hbox.Add(self.list, 1, wx.EXPAND) panel.SetSizer(hbox) self.Centre() self.Show(True)app = wx.App()Actresses(None, -1, 'actresses')app.MainLoop() |
wxpython widgets wx.html Help window
wxpython widgets wx.html Help window
wx.html.HtmlWindow to provide help in our application. We can create a standalone window or we can create a window that is going to be a part of the application. The following script will create a help window using the latter idea.
help.html
wx.html.HtmlWindow to provide help in our application. We can create a standalone window or we can create a window that is going to be a part of the application. The following script will create a help window using the latter idea.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 | import wximport wx.html as htmlclass HelpWindow(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, parent, id, title): wx.Frame.__init__(self, parent, id, title, size=(570, 400)) toolbar = self.CreateToolBar() toolbar.AddLabelTool(1, 'Exit', wx.Bitmap('img/quit.png')) toolbar.AddLabelTool(2, 'Help', wx.Bitmap('img/help.png')) toolbar.Realize() self.splitter = wx.SplitterWindow(self, -1) self.panelLeft = wx.Panel(self.splitter, -1, style=wx.BORDER_SUNKEN) self.panelRight = wx.Panel(self.splitter, -1) vbox2 = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL) header = wx.Panel(self.panelRight, -1, size=(-1, 20)) header.SetBackgroundColour('#6f6a59') header.SetForegroundColour('WHITE') hbox = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL) st = wx.StaticText(header, -1, 'Help', (5, 5)) font = st.GetFont() font.SetPointSize(9) st.SetFont(font) hbox.Add(st, 1, wx.TOP | wx.BOTTOM | wx.LEFT, 5) close = wx.BitmapButton(header, -1, wx.Bitmap('img/quit.png', wx.BITMAP_TYPE_PNG), style=wx.NO_BORDER) close.SetBackgroundColour('#6f6a59') hbox.Add(close, 0) header.SetSizer(hbox) vbox2.Add(header, 0, wx.EXPAND) help = html.HtmlWindow(self.panelRight, -1, style=wx.NO_BORDER) help.LoadPage('help.html') vbox2.Add(help, 1, wx.EXPAND) self.panelRight.SetSizer(vbox2) self.panelLeft.SetFocus() self.splitter.SplitVertically(self.panelLeft, self.panelRight) self.splitter.Unsplit() self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.CloseHelp, id=close.GetId()) self.Bind(wx.EVT_TOOL, self.OnClose, id=1) self.Bind(wx.EVT_TOOL, self.OnHelp, id=2) self.Bind(wx.EVT_KEY_DOWN, self.OnKeyPressed) self.CreateStatusBar() self.Centre() self.Show(True) def OnClose(self, event): self.Close() def OnHelp(self, event): self.splitter.SplitVertically(self.panelLeft, self.panelRight) self.panelLeft.SetFocus() def CloseHelp(self, event): self.splitter.Unsplit() self.panelLeft.SetFocus() def OnKeyPressed(self, event): keycode = event.GetKeyCode() if keycode == wx.WXK_F1: self.splitter.SplitVertically(self.panelLeft, self.panelRight) self.panelLeft.SetFocus()app = wx.App()HelpWindow(None, -1, 'HelpWindow')app.MainLoop() |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 | <h4>Table of Contents</h4><ul><li><a href="#basic">Basic statistics</a></li><li><a href="#advanced">Advanced statistics</a></li><li><a href="#intro">Introducing Newt</a></li><li><a href="#charts">Working with charts</a></li><li><a href="#pred">Predicting values</a></li><li><a href="#neural">Neural networks</a></li><li><a href="#glos">Glossary</a></li></ul><p><a name="basic"></a></p><h6><a name="basic">Basic Statistics</a></h6><a name="basic">Overview of elementary concepts in statistics.Variables. Correlation. Measurement scales. Statistical significance. Distributions. Normality assumption.</a><p></p><p><a name="advanced"></a></p><h6><a name="advanced">Advanced Statistics</a></h6><a name="advanced">Overview of advanced concepts in statistics. Anova. Linear regression. Estimation and hypothesis testing.Error terms.</a><p></p><p><a name="intro"></a></p><h6><a name="intro">Introducing Newt</a></h6><a name="intro">Introducing the basic functionality of the Newt application. Creating sheets. Charts. Menus and Toolbars. Importing data. Saving data in various formats. Exporting data. Shortcuts. List of methods.</a><p></p><p><a name="charts"></a></p><h6><a name="charts">Charts</a></h6><a name="charts">Working with charts. 2D charts. 3D charts. Bar, line, box, pie, range charts. Scatterplots. Histograms.</a><p></p><p><a name="pred"></a></p><h6><a name="pred">Predicting values</a></h6><a name="pred">Time series and forecasting. Trend Analysis. Seasonality. Moving averages. Univariate methods. Multivariate methods. Holt-Winters smoothing. Exponential smoothing. ARIMA. Fourier analysis.</a><p></p><p><a name="neural"></a></p><h6><a name="neural">Neural networks</a></h6><a name="neural">Overview of neural networks. Biology behind neural networks.Basic artificial Model. Training. Preprocessing. Postprocessing. Types of neural networks.</a><p></p><p><a name="glos"></a></p><h6><a name="glos">Glossary</a></h6><a name="glos">Terms and definitions in statistics.</a><p></p> |
wxpython widgets wx.html.HtmlWindow
wxpython widgets wx.html.HtmlWindow
The wx.html.HtmlWindow widget displays HTML pages. It is not a full-fledged browser. We can do interesting things with wx.html.HtmlWindow widget.
The wx.html.HtmlWindow widget displays HTML pages. It is not a full-fledged browser. We can do interesting things with wx.html.HtmlWindow widget.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 | import wximport wx.html as htmlID_CLOSE = 1page = ' \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \<table cellspacing="5" border="0" width="250"><tbody><tr width="200" align="left"><td bgcolor="#e7e7e7"> Maximum</td><td bgcolor="#aaaaaa"> <b>9000</b></td></tr><tr align="left"><td bgcolor="#e7e7e7"> Mean</td><td bgcolor="#aaaaaa"> <b>6076</b></td></tr><tr align="left"><td bgcolor="#e7e7e7"> Minimum</td><td bgcolor="#aaaaaa"> <b>3800</b></td></tr><tr align="left"><td bgcolor="#e7e7e7"> Median</td><td bgcolor="#aaaaaa"> <b>6000</b></td></tr><tr align="left"><td bgcolor="#e7e7e7"> Standard Deviation</td><td bgcolor="#aaaaaa"> <b>6076</b></td></tr></tbody></table>'class MyFrame(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, parent, id, title): wx.Frame.__init__(self, parent, id, title, size=(400, 290)) panel = wx.Panel(self, -1) vbox = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL) hbox = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL) htmlwin = html.HtmlWindow(panel, -1, style=wx.NO_BORDER) htmlwin.SetBackgroundColour(wx.RED) htmlwin.SetStandardFonts() htmlwin.SetPage(page) vbox.Add((-1, 10), 0) vbox.Add(htmlwin, 1, wx.EXPAND | wx.ALL, 9) bitmap = wx.StaticBitmap(panel, -1, wx.Bitmap('img/sales.png')) hbox.Add(bitmap, 1, wx.LEFT | wx.BOTTOM | wx.TOP, 10) buttonOk = wx.Button(panel, ID_CLOSE, 'Ok') self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnClose, id=ID_CLOSE) hbox.Add((100, -1), 1, wx.EXPAND | wx.ALIGN_RIGHT) hbox.Add(buttonOk, flag=wx.TOP | wx.BOTTOM | wx.RIGHT, border=10) vbox.Add(hbox, 0, wx.EXPAND) panel.SetSizer(vbox) self.Centre() self.Show(True) def OnClose(self, event): self.Close()app = wx.App(0)MyFrame(None, -1, 'Basic Statistics')app.MainLoop() |
Saturday, June 4, 2016
wxpython advance widgets wx.ListBox
wxpython advance widgets wx.ListBox
A wx.ListBox widget is used for displaying and working with a list of items
A wx.ListBox widget is used for displaying and working with a list of items
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 | import wxID_NEW = 1ID_RENAME = 2ID_CLEAR = 3ID_DELETE = 4class ListBox(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, parent, id, title): wx.Frame.__init__(self, parent, id, title, size=(350, 220)) panel = wx.Panel(self, -1) hbox = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL) self.listbox = wx.ListBox(panel, -1) #create an empty wx.ListBox hbox.Add(self.listbox, 1, wx.EXPAND | wx.ALL, 20) # put a 20px border around the listbox btnPanel = wx.Panel(panel, -1) vbox = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL) new = wx.Button(btnPanel, ID_NEW, 'New', size=(90, 30)) ren = wx.Button(btnPanel, ID_RENAME, 'Rename', size=(90, 30)) dlt = wx.Button(btnPanel, ID_DELETE, 'Delete', size=(90, 30)) clr = wx.Button(btnPanel, ID_CLEAR, 'Clear', size=(90, 30)) self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.NewItem, id=ID_NEW) self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnRename, id=ID_RENAME) self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnDelete, id=ID_DELETE) self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnClear, id=ID_CLEAR) self.Bind(wx.EVT_LISTBOX_DCLICK, self.OnRename) #bind a wx.EVT_COMMAND_LISTBOX_DOUBLE_CLICKED event type with the OnRename() method vbox.Add((-1, 20)) vbox.Add(new) vbox.Add(ren, 0, wx.TOP, 5) vbox.Add(dlt, 0, wx.TOP, 5) vbox.Add(clr, 0, wx.TOP, 5) btnPanel.SetSizer(vbox) hbox.Add(btnPanel, 0.6, wx.EXPAND | wx.RIGHT, 20) panel.SetSizer(hbox) self.Centre() self.Show(True) def NewItem(self, event): text = wx.GetTextFromUser('Enter a new item', 'Insert dialog') if text != '': self.listbox.Append(text) def OnRename(self, event): sel = self.listbox.GetSelection() text = self.listbox.GetString(sel) renamed = wx.GetTextFromUser('Rename item', 'Rename dialog', text) if renamed != '': self.listbox.Delete(sel) self.listbox.Insert(renamed, sel) def OnDelete(self, event): sel = self.listbox.GetSelection() if sel != -1: self.listbox.Delete(sel) def OnClear(self, event): self.listbox.Clear()app = wx.App()ListBox(None, -1, 'ListBox')app.MainLoop() |
wxpython widgets wx.SpinCtrl
wxpython widgets wx.SpinCtrl
The wx.SpinCtrl widget lets us increment and decrement a value. It has two up and down arrow buttons for this purpose.
The wx.SpinCtrl widget lets us increment and decrement a value. It has two up and down arrow buttons for this purpose.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 | import wxclass Example(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, *args, **kw): super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw) self.InitUI() def InitUI(self): pnl = wx.Panel(self) wx.StaticText(self, label='Convert Fahrenheit temperature to Celsius', pos=(20,20)) wx.StaticText(self, label='Fahrenheit: ', pos=(20, 80)) wx.StaticText(self, label='Celsius: ', pos=(20, 150)) self.celsius = wx.StaticText(self, label='', pos=(150, 150)) self.sc = wx.SpinCtrl(self, value='0', pos=(150, 75), size=(60, -1)) self.sc.SetRange(-459, 1000) btn = wx.Button(self, label='Compute', pos=(70, 230)) btn.SetFocus() cbtn = wx.Button(self, label='Close', pos=(185, 230)) btn.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnCompute) cbtn.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnClose) self.SetSize((350, 310)) self.SetTitle('wx.SpinCtrl') self.Centre() self.Show(True) def OnClose(self, e): self.Close(True) def OnCompute(self, e): fahr = self.sc.GetValue() cels = round((fahr - 32) * 5 / 9.0, 2) self.celsius.SetLabel(str(cels)) def main(): ex = wx.App() Example(None) ex.MainLoop() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
wxpython widgets wx.Slider
wxpython widgets wx.Slider
wx.Slider is a widget that has a simple handle. This handle can be pulled back and forth. This way we can choose a specific task.
wx.Slider is a widget that has a simple handle. This handle can be pulled back and forth. This way we can choose a specific task.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 | import wxclass Example(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, *args, **kw): super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw) self.InitUI() def InitUI(self): pnl = wx.Panel(self) sld = wx.Slider(pnl, value=200, minValue=150, maxValue=500, pos=(20, 20), size=(250, -1), style=wx.SL_HORIZONTAL) sld.Bind(wx.EVT_SCROLL, self.OnSliderScroll) self.txt = wx.StaticText(pnl, label='200', pos=(20, 90)) self.SetSize((290, 200)) self.SetTitle('wx.Slider') self.Centre() self.Show(True) def OnSliderScroll(self, e): obj = e.GetEventObject() val = obj.GetValue() self.txt.SetLabel(str(val)) def main(): ex = wx.App() Example(None) ex.MainLoop() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
wxpython widgets wx.Gauge
wxpython widgets wx.Gauge
wx.Gauge is a widget that is used, when we process lengthy tasks. It has an indicator to show the current state of a task.
wx.Gauge is a widget that is used, when we process lengthy tasks. It has an indicator to show the current state of a task.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 | import wxTASK_RANGE = 50class Example(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, *args, **kw): super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw) self.InitUI() def InitUI(self): self.timer = wx.Timer(self, 1) self.count = 0 self.Bind(wx.EVT_TIMER, self.OnTimer, self.timer) pnl = wx.Panel(self) vbox = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL) hbox1 = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL) hbox2 = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL) hbox3 = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL) self.gauge = wx.Gauge(pnl, range=TASK_RANGE, size=(250, 25)) self.btn1 = wx.Button(pnl, wx.ID_OK) self.btn2 = wx.Button(pnl, wx.ID_STOP) self.text = wx.StaticText(pnl, label='Task to be done') self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnOk, self.btn1) self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnStop, self.btn2) hbox1.Add(self.gauge, proportion=1, flag=wx.ALIGN_CENTRE) hbox2.Add(self.btn1, proportion=1, flag=wx.RIGHT, border=10) hbox2.Add(self.btn2, proportion=1) hbox3.Add(self.text, proportion=1) vbox.Add((0, 30)) vbox.Add(hbox1, flag=wx.ALIGN_CENTRE) vbox.Add((0, 20)) vbox.Add(hbox2, proportion=1, flag=wx.ALIGN_CENTRE) vbox.Add(hbox3, proportion=1, flag=wx.ALIGN_CENTRE) pnl.SetSizer(vbox) self.SetSize((300, 200)) self.SetTitle('wx.Gauge') self.Centre() self.Show(True) def OnOk(self, e): if self.count >= TASK_RANGE: return self.timer.Start(100) self.text.SetLabel('Task in Progress') def OnStop(self, e): if self.count == 0 or self.count >= TASK_RANGE or not self.timer.IsRunning(): return self.timer.Stop() self.text.SetLabel('Task Interrupted') def OnTimer(self, e): self.count = self.count + 1 self.gauge.SetValue(self.count) if self.count == TASK_RANGE: self.timer.Stop() self.text.SetLabel('Task Completed') def main(): ex = wx.App() Example(None) ex.MainLoop() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
wxpython widgets wx.RadioButton
wxpython widgets wx.RadioButton
wx.RadioButton is a widget that allows the user to select a single exclusive choice from a group of options.
wx.RadioButton is a widget that allows the user to select a single exclusive choice from a group of options.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 | import wxclass Example(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, *args, **kw): super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw) self.InitUI() def InitUI(self): pnl = wx.Panel(self) self.rb1 = wx.RadioButton(pnl, label='Value A', pos=(10, 10), style=wx.RB_GROUP) self.rb2 = wx.RadioButton(pnl, label='Value B', pos=(10, 30)) self.rb3 = wx.RadioButton(pnl, label='Value C', pos=(10, 50)) self.rb1.Bind(wx.EVT_RADIOBUTTON, self.SetVal) self.rb2.Bind(wx.EVT_RADIOBUTTON, self.SetVal) self.rb3.Bind(wx.EVT_RADIOBUTTON, self.SetVal) self.sb = self.CreateStatusBar(3) self.sb.SetStatusText("True", 0) self.sb.SetStatusText("False", 1) self.sb.SetStatusText("False", 2) self.SetSize((210, 210)) self.SetTitle('wx.RadioButton') self.Centre() self.Show(True) def SetVal(self, e): state1 = str(self.rb1.GetValue()) state2 = str(self.rb2.GetValue()) state3 = str(self.rb3.GetValue()) self.sb.SetStatusText(state1, 0) self.sb.SetStatusText(state2, 1) self.sb.SetStatusText(state3, 2) def main(): ex = wx.App() Example(None) ex.MainLoop() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
wxpython widgets wx.StatusBar
wxpython widgets wx.StatusBar
wx.StatusBar widget is used to display application status information.
wx.StatusBar widget is used to display application status information.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 | import wxclass Example(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, *args, **kw): super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw) self.InitUI() def InitUI(self): pnl = wx.Panel(self) button = wx.Button(pnl, label='Button', pos=(20, 20)) text = wx.CheckBox(pnl, label='CheckBox', pos=(20, 90)) combo = wx.ComboBox(pnl, pos=(120, 22), choices=['Python', 'Ruby']) slider = wx.Slider(pnl, 5, 6, 1, 10, (120, 90), (110, -1)) pnl.Bind(wx.EVT_ENTER_WINDOW, self.OnWidgetEnter) button.Bind(wx.EVT_ENTER_WINDOW, self.OnWidgetEnter) text.Bind(wx.EVT_ENTER_WINDOW, self.OnWidgetEnter) combo.Bind(wx.EVT_ENTER_WINDOW, self.OnWidgetEnter) slider.Bind(wx.EVT_ENTER_WINDOW, self.OnWidgetEnter) self.sb = self.CreateStatusBar() self.SetSize((250, 230)) self.SetTitle('wx.Statusbar') self.Centre() self.Show(True) def OnWidgetEnter(self, e): name = e.GetEventObject().GetClassName() self.sb.SetStatusText(name + ' widget') e.Skip() def main(): ex = wx.App() Example(None) ex.MainLoop() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
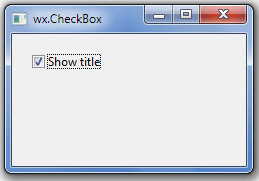
wxpython widgets wx.CheckBox
wxpython widgets wx.CheckBox
wx.CheckBox is a widget that has two states: on and off. It is a box with a label. The label can be set to the right or to the left of the box.
wx.CheckBox is a widget that has two states: on and off. It is a box with a label. The label can be set to the right or to the left of the box.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 | import wxclass Example(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, *args, **kw): super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw) self.InitUI() def InitUI(self): pnl = wx.Panel(self) cb = wx.CheckBox(pnl, label='Show title', pos=(20, 20)) cb.SetValue(True) #constructor of the wx.CheckBox widget cb.Bind(wx.EVT_CHECKBOX, self.ShowOrHideTitle) self.SetSize((250, 170)) self.SetTitle('wx.CheckBox') self.Centre() self.Show(True) def ShowOrHideTitle(self, e): sender = e.GetEventObject() isChecked = sender.GetValue() if isChecked: self.SetTitle('wx.CheckBox') else: self.SetTitle('') def main(): ex = wx.App() Example(None) ex.MainLoop() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
wxpython widgets wx.ComboBox
wxpython widgets wx.ComboBox
wx.ComboBox is a combination of a single line text field, a button with a down arrow image and a listbox. When you press the button, a listbox appears.
wx.ComboBox is a combination of a single line text field, a button with a down arrow image and a listbox. When you press the button, a listbox appears.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | import wxclass Example(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, *args, **kw): super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw) self.InitUI() def InitUI(self): pnl = wx.Panel(self) distros = ['Ubuntu', 'Arch', 'Fedora', 'Debian', 'Mint'] cb = wx.ComboBox(pnl, pos=(50, 30), choices=distros, style=wx.CB_READONLY) self.st = wx.StaticText(pnl, label='', pos=(50, 140)) cb.Bind(wx.EVT_COMBOBOX, self.OnSelect) self.SetSize((250, 230)) self.SetTitle('wx.ComboBox') self.Centre() self.Show(True) def OnSelect(self, e): i = e.GetString() self.st.SetLabel(i) def main(): ex = wx.App() Example(None) ex.MainLoop() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
wxpython widgets wx.StaticBox
wxpython widgets wx.StaticBox
This is a kind of a decorator widget. It is used to logically group various widgets.
This is a kind of a decorator widget. It is used to logically group various widgets.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 | import wxclass Example(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, *args, **kw): super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw) self.InitUI() def InitUI(self): pnl = wx.Panel(self) wx.StaticBox(pnl, label='Personal Info', pos=(5, 5), size=(240, 170)) wx.CheckBox(pnl, label='Male', pos=(15, 30)) wx.CheckBox(pnl, label='Married', pos=(15, 55)) wx.StaticText(pnl, label='Age', pos=(15, 95)) wx.SpinCtrl(pnl, value='1', pos=(55, 90), size=(60, -1), min=1, max=120) btn = wx.Button(pnl, label='Ok', pos=(90, 185), size=(60, -1)) btn.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnClose) self.SetSize((270, 250)) self.SetTitle('Static box') self.Centre() self.Show(True) def OnClose(self, e): self.Close(True) def main(): ex = wx.App() Example(None) ex.MainLoop() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
wxpython widgets wx.StaticText
wxpython widgets wx.StaticText
A wx.StaticText widget displays one or more lines of read-only text.
A wx.StaticText widget displays one or more lines of read-only text.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 | import wxclass Example(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, *args, **kw): super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw) self.InitUI() def InitUI(self): txt1 = '''I'm giving up the ghost of lovein the shadows cast on devotionShe is the one that I adorecreed of my silent suffocationBreak this bittersweet spell on melost in the arms of destiny''' txt2 = '''There is something in the wayYou're always somewhere elseFeelings have deserted meTo a point of no returnI don't believe in GodBut I pray for you''' pnl = wx.Panel(self) vbox = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL) st1 = wx.StaticText(pnl, label=txt1, style=wx.ALIGN_CENTRE) st2 = wx.StaticText(pnl, label=txt2, style=wx.ALIGN_CENTRE) vbox.Add(st1, flag=wx.ALL, border=5) vbox.Add(st2, flag=wx.ALL, border=5) pnl.SetSizer(vbox) self.SetSize((250, 260)) self.SetTitle('Bittersweet') self.Centre() self.Show(True) def main(): ex = wx.App() Example(None) ex.MainLoop() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
Saturday, May 28, 2016
wxpython widgets wx.StaticText
wxpython widgets wx.StaticText
A wx.StaticText widget displays one or more lines of read-only text.
A wx.StaticText widget displays one or more lines of read-only text.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 | import wxclass Example(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, *args, **kw): super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw) self.InitUI() def InitUI(self): txt1 = '''I'm giving up the ghost of lovein the shadows cast on devotionShe is the one that I adorecreed of my silent suffocationBreak this bittersweet spell on melost in the arms of destiny''' txt2 = '''There is something in the wayYou're always somewhere elseFeelings have deserted meTo a point of no returnI don't believe in GodBut I pray for you''' pnl = wx.Panel(self) #create panel vbox = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL) #This is a string to be shown in the wx.StaticText widget. #wx.StaticText(variable panel,lable,style) st1 = wx.StaticText(pnl, label=txt1, style=wx.ALIGN_CENTRE) st2 = wx.StaticText(pnl, label=txt2, style=wx.ALIGN_CENTRE) vbox.Add(st1, flag=wx.ALL, border=5) vbox.Add(st2, flag=wx.ALL, border=5) pnl.SetSizer(vbox) self.SetSize((250, 260)) self.SetTitle('Bittersweet') self.Centre() self.Show(True) def main(): ex = wx.App() Example(None) ex.MainLoop() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
wxpython widgets wx.StaticLine
wxpython widgets wx.StaticLine
This widget displays a simple line on the window. It can be horizontal or vertical.
This widget displays a simple line on the window. It can be horizontal or vertical.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 | import wxclass Example(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, *args, **kw): super(Example, self).__init__(*args, **kw) self.InitUI() #call function def InitUI(self): def InitUI(self): pnl = wx.Panel(self) #create panel font = wx.Font(10, wx.DEFAULT, wx.NORMAL, wx.BOLD) heading = wx.StaticText(self, label='The Central Europe', pos=(130, 15)) heading.SetFont(font) wx.StaticLine(self, pos=(25, 50), size=(300,1)) wx.StaticText(self, label='Slovakia', pos=(25, 80)) wx.StaticText(self, label='Hungary', pos=(25, 100)) wx.StaticText(self, label='Poland', pos=(25, 120)) wx.StaticText(self, label='Czech Republic', pos=(25, 140)) wx.StaticText(self, label='Germany', pos=(25, 160)) wx.StaticText(self, label='Slovenia', pos=(25, 180)) wx.StaticText(self, label='Austria', pos=(25, 200)) wx.StaticText(self, label='Switzerland', pos=(25, 220)) wx.StaticText(self, label='5 445 000', pos=(250, 80)) wx.StaticText(self, label='10 014 000', pos=(250, 100)) wx.StaticText(self, label='38 186 000', pos=(250, 120)) wx.StaticText(self, label='10 562 000', pos=(250, 140)) wx.StaticText(self, label='81 799 000', pos=(250, 160)) wx.StaticText(self, label='2 050 000', pos=(250, 180)) wx.StaticText(self, label='8 414 000', pos=(250, 200)) wx.StaticText(self, label='7 866 000', pos=(250, 220)) wx.StaticLine(self, pos=(25, 260), size=(300,1)) tsum = wx.StaticText(self, label='164 336 000', pos=(240, 280)) sum_font = tsum.GetFont() sum_font.SetWeight(wx.BOLD) tsum.SetFont(sum_font) btn = wx.Button(self, label='Close', pos=(140, 310)) btn.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnClose) self.SetSize((360, 380)) self.SetTitle('wx.StaticLine')#form panel title self.Centre() self.Show(True) def OnClose(self, e): self.Close(True) def main(): ex = wx.App() Example(None) ex.MainLoop() if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)